순열 permutation
순서를 따짐, 시간 복잡도 O(n!)
[1,2,3]의 순열
[ [ 1, 2 ], [ 1, 3 ], [ 2, 1 ], [ 2, 3 ], [ 3, 1 ], [ 3, 2 ] ]
function getPermutation(arr, count) {
if (count === 1) {
return arr.map((e) => [e]);
}
const result = [];
arr.forEach((selected) => {
const rest = arr.filter((e) => e !== selected);
// 선택된 걸 제외한 남은 것들로 만든 순열을 구한다
const newPermutation = getPermutation(rest, count - 1);
// 선택된것과 남은 것으로 만들어진 순열을 합친다
newPermutation.forEach((newPer) => {
result.push([selected, ...newPer]);
});
});
return result;
}
조합 combination
순서 상관없음
시간복잡도 O(2^n-1) 존재하나 마나가 요점, 지수시간 복잡도를 갖기 떄문에 백트래킹, dp가 효율적
[1,2,3]의 조합
[ [ 1, 2 ], [ 1, 3 ], [ 2, 3 ] ]
function getCombination(arr, count) {
if (count === 1) {
return arr.map((e) => [e]);
}
const result = [];
arr.forEach((selected, i) => {
const rest = arr.slice(i + 1); // 이 부분이 순열과 다름 (선택된 것 이전은 고르지 않음)
const newCombi = getCombination(rest, count - 1);
newCombi.forEach((newCombi) => {
result.push([selected, ...newCombi]);
});
});
return result;
}
console.log(getCombination([1, 2, 3], 2)); // [ [ 1, 2 ], [ 1, 3 ], [ 2, 3 ] ]
완전탐색 (각 갯수마다 순열) permuteSubset
[1,2,3] 의 완전탐색
[1],[2],[3],
[1,2],[2,1],[2,3],[3,2],[1,3],[3,1],
[1,2,3],[2,1,3],[2,3,1]function getPermutSubset(arr) {
const set = new Set();
function dfs(arr, subset) {
if (arr.length) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
let copy = [...arr];
copy.splice(i, 1);
dfs(copy, subset + arr[i]);
}
}
if (subset.length > 0) set.add(Number(subset));
}
dfs(arr, "");
return Array.from(set);
}
console.log(getPermutSubset([1, 5])); // [ 15, 1, 51, 5 ]
부분집합 (각 갯수마다 조합) combiSubset
[1,2,3] 의 부분 집합은 순서 상관없다
[1], [2], [3], [1, 2], [2, 3], [1, 3], [1, 2, 3]
원소 갯수가 1개, 2개, 3개인 조합
한 원소 당 존재 / 존재 하지 않는 2가지의 경우가 있다
따라서 n개의 수로 만들 수 있는 부분집합은 2^n - 1개이다
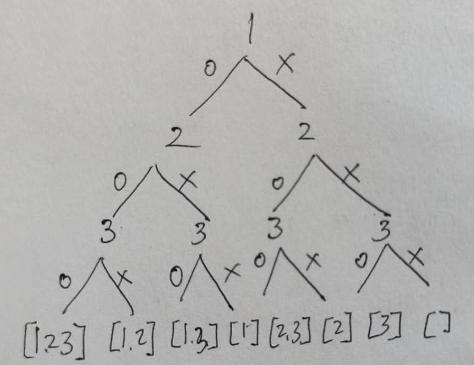
dfs 방법1
function getCombiSubset(arr) {
const result = [];
function dfs(rest, curr) {
if (!rest.length) {
result.push(curr);
return;
}
const newRest = [...rest];
const now = newRest.shift();
dfs(newRest, [...curr, now]); // 존재
dfs(newRest, curr); // 존재x
}
-
dfs(arr, []);
result.pop();
return result;
}
console.log(getCombiSubset([1, 2, 3])); // [ [ 1, 2, 3 ], [ 1, 2 ], [ 1, 3 ], [ 1 ], [ 2, 3 ], [ 2 ], [ 3 ] ]
dfs 방법2
const getCombiSubset = (arr) => {
const result = [];
function dfs(start, subset) {
result.push(subset);
for (let i = start; i < arr.length; i++) {
dfs(i + 1, [...subset, arr[i]]);
}
}
dfs(0, []);
return result; // [[], [1], [1, 2], [1, 2, 3], [1, 3], [2], [2, 3], [3]];
};비트 연산자 방법
비트 시프트 연산자 <<, >>
console.log(5 << 2); // 101 => 10100 => 20
console.log(5 >> 2); // 101 => 1 => 1
console.log(1 << 3); // 1 => 1000 => 8
function getSubset(arr) {
let result = [];
const max = 1 << arr.length;
for (let i = 1; i < max; i++) {
result.push([]);
for (let j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (i & (1 << j)) {
result[i - 1].push(arr[j]);
}
}
}
return result;
}
console.log(getSubset([1, 2, 3])); // [ [ 1 ], [ 2 ], [ 1, 2 ], [ 3 ], [ 1, 3 ], [ 2, 3 ], [ 1, 2, 3 ] ]
[JavaScript] 자바스크립트 연산자 정리(비트, 논리 연산자)
프로그래밍 문법 중에서 가장 기본이 되는 부분은 당연히 연산자 사용 방법이라고 생각합니다. 그만큼, 사용하는 것에 있어서 어렵지 않지만, 잘 써야하고, 많이 쓰는 부분이기 때문입니다. 이
blankspace-dev.tistory.com
백트래킹
모든경우의 수를 하나씩 탐색하는데
가능성이 없는 후보들은 더 이상 탐색하지 않고 뒤로 돌아가고, 가능한 것들만 탐색한다.
var subsets = function(nums) {
const answer = [];
function bt(index, letter) {
if (index === nums.length) {
answer.push(letter);
return;
}
const char = nums[index];
bt(index+1, letter); // 선택 안 된
bt(index+1, [...letter, char]); // 선택 된
}
bt(0, []);
return answer;
};
백트래킹, 브루트포스를 구별하는 특징?
백트래킹은
- 모든 가능한 후보를 탐색 (유효한 후보가 아니면 이전단계로 백트랙)
- 주로 dfs기반 (뒤로 돌아가야하니까)
- n queens, 스도쿠문제
브루트포스
- 단순 반복, 조건문으로 모든 경우를 탐색
- 모든 가능한 조합을 순차적으로 생성, 조건을 만족하는지 확인
- 간단하고 직관적이지만 수가 많으면 비효율적
정리하자면 백트래킹은 불필요한 탐색을 줄이기 위해 가지치기 (pruning)을하지만,
브루트포스는 단순히 모든 경우를 시도하고 확인한다
따라서 백트래킹이 더 효율적이다
'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Softeer] 사물인식 최소 면적 산출 프로그램 JS (0) | 2024.02.01 |
|---|---|
| [Softeer] 택배 마스터 광우 JS (0) | 2024.01.31 |
| [Softeer] 동계 테스트 시점 예측 JS (0) | 2024.01.31 |
| [Softeer] 통근버스 출발 순서 검증하기 JS (0) | 2024.01.30 |
| [Softeer] 진정한 효도 JS (0) | 2024.01.30 |



